For example, to get the processor specifications, type the following command:
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo
This is a very powerful and easy way to query Linux kernel.
Notice that if you check the size of the file in /proc directory, you will find that all file sizes are 0, because as we said they don’t exist on the disk.
When you type cat /proc/cpuinfo command, a file is dynamically created to show you the CPU info.
The only file that has a size in /proc directory is /proc/kcore file, which shows the RAM content. Actually, this file isn’t occupying any space on the disk.
Writing to Proc Files
As we’ve seen, we can read the content of proc files, but some of them are writable, so we can write to them to change some functionality.
For example, this /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward file controls IP forwarding in case you have multiple network cards.
You can change the value of this file like this:
$ echo "1" > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Keep in mind that when you change any file or value under /proc directory there is no validation of what you are doing, you may crash your system if you type a wrong setting.
Persisting /proc Files Changes
The previous modification to the /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward entry will not survive after rebooting since you are not writing to a file, this is a virtual file system, means change happens to the memory.
If you need to save changes under /proc, you have two ways:
- You can write your entries in /etc/rc.local file, or in Red Hat based distros like CentOS, create /etc/rc.d/rc.local file and make it executable and enable the systemd service unit that enables the use of the rc.local file and write your entries.
- The sysctl command is used to change entries in /proc/sys/ directory.
$ sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward
This will show the value of the entry, to change it, use the -w option:
$ sysctl –w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
One final step is to write the changes to /etc/sysctl.conf:
$ echo “net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1” >> /etc/sysctl.conf
Make sure that the file /etc/sysctl.conf does not contain the entry before you write your changes.
Common /proc Entries
These are some of the commonly used /proc entries:
/proc/cpuinfo information about CPUs in the system.
/proc/meminfo information about memory usage.
/proc/ioports list of port regions used for I/O communication with devices.
/proc/mdstat display the status of RAID disks configuration.
/proc/kcore displays the system actual memory.
/proc/modules displays a list of kernel loaded modules.
/proc/cmdline displays the passed boot parameters.
/proc/swaps displays the status of swap partitions.
/proc/iomem the current map of the system memory for each physical device.
/proc/version displays the kernel version and time of compilation.
/proc/net/dev displays information about each network device like packets count.
/proc/net/sockstat displays statistics about network socket utilization.
/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_ display the range of ports that Linux uses.
local_port_range
/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ protection against syn flood attacks.
tcp_ syncookies
These are some of the common entries in /proc directory.
Listing /proc Directory
If you list the files in /proc directory, you’ll notice a lot of directories which have numeric names, these directories contain information about the running processes and the numeric value is the corresponding process ID.
You can check the consumed resources by a specific process from these directories.
If you take a look at the folder named 1, it belongs to the init process or systemd (like CentOS 7) which is the first process runs When Linux starts.
$ ls -l /proc/1

The /proc/1/exe file is a symbolic link to /lib/systemd/systemd binary or /sbin/init in other systems that use init binary.
The same concept applies to all numeric folders under /proc directory.
proc Useful Examples
To protect your server from SYN flood attack, you can use iptables to block SYN packets.
A better solution is to use SYN cookies. A special method in the kernel that keeps track of which SYN packets come. If the SYN packets don’t move to established state within a reasonable interval, the kernel will drop them.
$ sysctl -w net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies=1
And to persist the changes.
$ echo "net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
Another useful example which is the /proc/sys/fs/file-max, this value shows the maximum files (including sockets, files, etc,) that can be opened at the same time.
You can increase this number like this:
$ sysctl -w "fs.file-max=96992"
$ echo "fs.file-max = 96992" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
sysfs Virtual File System
sysfs is a Linux virtual file systems which mean it’s also in memory.
sysfs file system can be found at /sys. The sysfs can be used to get information about your system hardware.
$ ls -l /sys
From the result of the above command, the file sizes are all zero because as we know this is a Linux virtual file system.
The top level directory of /sys contains the following:
Block list of block devices detected on the system like sda.
Bus contains subdirectories for physical buses detected in the kernel.
class describes class of device like audio, network or printer.
Devices list all detected devices by the physical bus registered with the kernel.
Module lists all loaded modules.
Power the power state of your devices.
tmpfs Virtual File System
tmpfs is a Linux virtual file system that keeps data in the system virtual memory. It is the same like any other Virtual File Systems, any files are temporarily stored in the Kernel’s internal caches.
The /tmp file system is used as the storage location for temporary files.
The /tmp file system is backed by an actual disk-based storage and not by a virtual system.
This location is chosen during Linux installation.
The /tmp is created automatically by systemd service when booting the system.
You can setup tmpfs style file system with the size you want, using the mount command.
$ mount it tmpfs -o size=2GB tmpfs /home/myfolder
Awesome!!
Working with Linux virtual file system is very easy.
I hope you find the post useful and interesting. Keep coming back.
Thank you.
likegeeks.com
 Bir bakım (bir sistem kurtarma live CD’si gibi), multimedya, (inetd daemon kullanarak) bir miniserver gibi temel unsurlara odaklanan ve bazı küçük GNU/Linux oyunları sağlayan 4MLinux’un birkaç yeni özellik ile birlikte gelen kararlı sürümü 23.1 duyuruldu. 4.9.61 Linux çekirdeği üzerine yapılandırılan sistem; Apache 2.4.29, MariaDB 10.2.10 ve PHP 7.0.25 gibi güncel yazılımlar içeriyor. 4MLinux kullanıcılarının terminalde “zk update” komutunu çalıştırmak suretiyle sistemlerini kolaylıkla güncelleyebilecekleri ifade ediliyor. FAAC, GIF, JPEG 2000, Monkey’s Audio ve Musepack dosya formatları için geliştirilmiş destek sunan sürüm, SCSI, RAID ve LVM aygıtları için tam destek veriyor. 4MLinux 23.1 hakkında ayrıntılı bilgi edinmek üzere sürüm duyurusunu inceleyebilirsiniz.
Bir bakım (bir sistem kurtarma live CD’si gibi), multimedya, (inetd daemon kullanarak) bir miniserver gibi temel unsurlara odaklanan ve bazı küçük GNU/Linux oyunları sağlayan 4MLinux’un birkaç yeni özellik ile birlikte gelen kararlı sürümü 23.1 duyuruldu. 4.9.61 Linux çekirdeği üzerine yapılandırılan sistem; Apache 2.4.29, MariaDB 10.2.10 ve PHP 7.0.25 gibi güncel yazılımlar içeriyor. 4MLinux kullanıcılarının terminalde “zk update” komutunu çalıştırmak suretiyle sistemlerini kolaylıkla güncelleyebilecekleri ifade ediliyor. FAAC, GIF, JPEG 2000, Monkey’s Audio ve Musepack dosya formatları için geliştirilmiş destek sunan sürüm, SCSI, RAID ve LVM aygıtları için tam destek veriyor. 4MLinux 23.1 hakkında ayrıntılı bilgi edinmek üzere sürüm duyurusunu inceleyebilirsiniz.

 Video
Video  LibreOffice’in 5.4.4 serisinin ilk sürüm adayı
LibreOffice’in 5.4.4 serisinin ilk sürüm adayı 
 Uygulamaların oluşturulmasını hızlandırmak için tasarlanmış araçlar, masaüstü ortamları, gömülü ve mobil aygıtlar için kullanıcı arabirimleri içeren yetkin bir geliştirme platformu olan Qt’nin 5.10.0 sürümünün üçüncü sürüm adayı, Jani Heikkinen tarafından duyuruldu. Bunun bir test sürümü olduğunun unutulmaması ve yalnızca test etmek amacıyla kullanılması gerektiği hatırlatıldı ve test eden kullanıcıların tespit ettikleri hataları rapor etmeleri rica edildi.
Uygulamaların oluşturulmasını hızlandırmak için tasarlanmış araçlar, masaüstü ortamları, gömülü ve mobil aygıtlar için kullanıcı arabirimleri içeren yetkin bir geliştirme platformu olan Qt’nin 5.10.0 sürümünün üçüncü sürüm adayı, Jani Heikkinen tarafından duyuruldu. Bunun bir test sürümü olduğunun unutulmaması ve yalnızca test etmek amacıyla kullanılması gerektiği hatırlatıldı ve test eden kullanıcıların tespit ettikleri hataları rapor etmeleri rica edildi.  The Linux virtual file system or virtual file system generally is a layer that sits on the top of your actual file system which allows the user to access different types of file systems, you can think of virtual file system as an interface between the kernel and the actual file system. That means you will not find any entries for those Linux virtual filesystems in your /etc/fstab file. Yet, you will still find them when you type the mount command. If you are coming from Windows, the virtual file system is the Registry. The proc file system is a virtual file system which is mounted on /proc directory. There is no real file system exists on /proc, it’s a virtual layer that is used for dealing with the kernel functionalities.
The Linux virtual file system or virtual file system generally is a layer that sits on the top of your actual file system which allows the user to access different types of file systems, you can think of virtual file system as an interface between the kernel and the actual file system. That means you will not find any entries for those Linux virtual filesystems in your /etc/fstab file. Yet, you will still find them when you type the mount command. If you are coming from Windows, the virtual file system is the Registry. The proc file system is a virtual file system which is mounted on /proc directory. There is no real file system exists on /proc, it’s a virtual layer that is used for dealing with the kernel functionalities.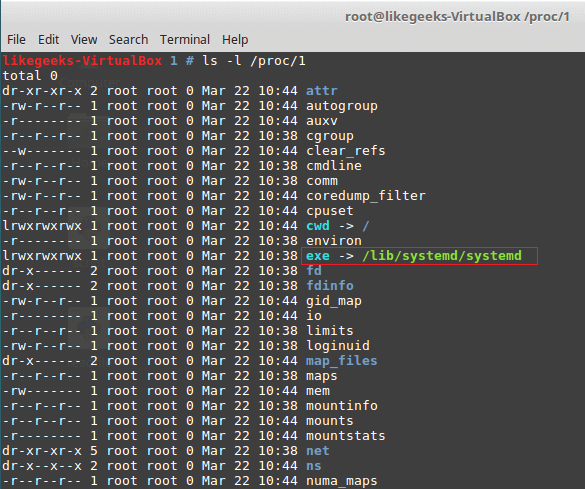
 Herhangi bir işletim sistemi normal yollarla önyükleme yapamadığında kullanıcıya yardımcı olması amacıyla tasarlanan
Herhangi bir işletim sistemi normal yollarla önyükleme yapamadığında kullanıcıya yardımcı olması amacıyla tasarlanan